Concept
Eductor are devices used to induce a secondary fluid by momentum and energy transfer from a high velocity primary jet. Eductor can be operated with incompressible fluids (liquids). On the other hand when Eductors are operated with compressible fluids (gases and vapors) the terms ejector and injector are generally employed. A major difference between the two, besides the working fluid states, is the supersonic, choked flow nozzle of the gas ejector system. The supersonic approach allows a greater conversion of primary fluid energy to secondary fluid pressure head increase.
Working principle
A high-pressure fluid with very low velocity at the primary inlet is accelerated to high velocity jet through a converging nozzle for the liquid jet or a converging-diverging supersonic nozzle for the gas ejector. The supply pressure at the inlet is partly converted to be the jet momentum at the nozzle exit according to the Bernoulli equation. The high velocity, low static pressure primary jet induces a secondary flow from the suction port and accelerates it in the direction of the driving jet. The two streams then combine in the mixing section, and ideally the process is complete by the end of this section.
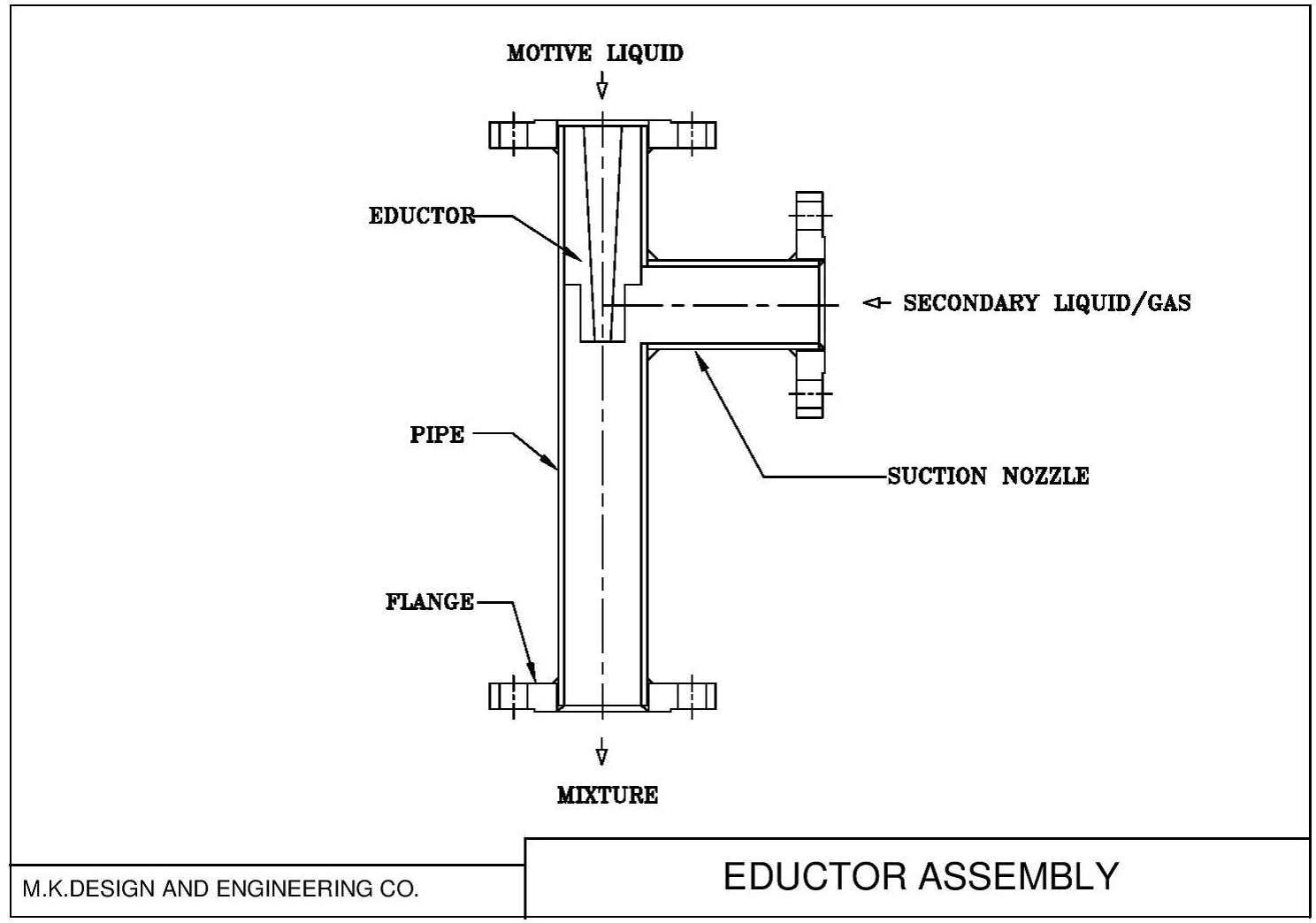
Parts of Eductor
- Housing or Pipe
- Nozzle for Motive Fluid
- Nozzle for Secondary fluid
- Eductor or Internal.
- Flange
- Discharge nozzle
Applications
- Creating vacuum that can be used to suck in other liquids for mixing, diluting or creating solution.
- Transferring powders and bulk solids.
- Can be used for slurry preparation.
- Emptying tank, sumps, pumping and mixing operation in chemical Industries.
- Eductor can be used in tanks for Agitation and mixing of liquid.
Advantages
- No Moving parts in the eductor make the installation simpler
- Lower capital cost and no maintence.
- Eductor can be use for High temperature Applications.
- Eductors are self priming.
- Eductors can be used in hazardous condition
Type of Eductors
Eductor are classifying base on their use and Construction as follows.
Design
Design or Selection of Tank Mixing Eductor and Eductor Jet Mixer are based on Process Parameters like Height of Tank, Diameter of Tank, liquid flow rate of pump and properties of fluid i.e. Density and Viscosity.
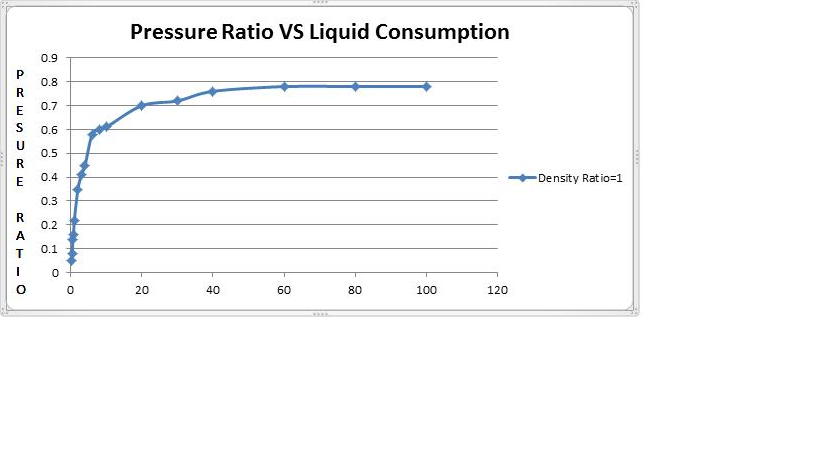
In Case of In-Line Eductor, Design is based on Motive fluid flow rate, required suction flow, Density ratio(D) (Density of Suction liquid/Density of Motive liquid), Pressure ratio(P) (Total Delivery pressure/ Effective Motive liquid pressure), and Specific liquid consumption (M)(Motive liquid in Kg / Suction Liquid in Kg).
We have plot a graph as shown below, Pressure Ratio Vs specific liquid Consumption. With the help of graph we can find out the specific liquid consumption (M) for particular Pressure Ratio, if the required process parameters are given as follows.
Design Standard
- ASME B31.3
- ASME B16.5
- ASME B16.47
- ASME SEC VIII DIV I
- ASME SEC VI DIV A/B/C
Material of Construction
- Carbon Steel
- Carbon Steel + FRP
- Carbon Steel + PVC
- Carbon Steel + Rubber Lined
- Carbon Steel + Epoxy Coating
- Stainless Steel ( SS 304,SS 304L,SS 316,SS 316L)
- Special Alloys
- Haste alloy
- Titanium